Net June 2012 Computer science and
applicationts Question paper with solutions
( UGC Net answer key for June 24, 2012 )
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
( UGC Net answer key for June 24, 2012 )
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
(1) Granulairity
refers to
(a) Size of a database
(b) Size of a data item
(c) Size of a record
(d) .........
Answer: (a) size of a data item
(2) R = (A, B, C, D). We
decompose it into R1 = (A, B), R2 = (C, D). The set of
functional dependencies
is: A → B, C → D, Then decomposition is a
(a) Dependency preserving but lossy
(b)Dependency preserving and
lossless
(c) lossless
(d) Neither lossy nor dependency
preserving
Answer: (b) Dependency preserving
but lossy
(3) if A(x) =
{0.1,0.2,0.3, .....}
B(x) = {0.3,0.4,0.5,......}
then find out Complement
of A ∩ B
Solution:
(1)find out Intersection first using
below rule
Standard intersection (A ∩ B)(x) =
min [A(x), B(x)]
(2) Find out complement using
complement rule
Standard complement cA(x) = 1 − A(x)
(4) Find out which of
the following grammer is in GNF(Greibach Normal Form )
Options: given 4 grammers and we
need to find out the grammers which are in GNF
(5) Find out the Regular
expression produced by the following DFA
(a) b(b*+a*b)
(b) a*b(b*+aa*b)*
Answer: (B)
(6) (1) Every
context-sensitive language is recursive
(2)
There exist recursive languages that are not context-sensitive
which of the following are
correct statements
(a) (1) only
(b) (2) only
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: (C)
Explanation:
Every regular language is
context-free, every context-free language is context-sensitive
and every context-sensitive language
is recursive and every recursive language is
recursively enumerable. These are
all proper inclusions, meaning that there exist
recursively enumerable languages
which are not recursive, recursive languages that are
not context-sensitive,
context-sensitive languages which are not context-free and contextfree
languages which are not regular.
(7) One Question on
the closure properties of Recursively enumarable languages, Recursive languages
and context free languages
Explanation:
if n=0, then DFA should accept only epsilon .....
total 2 states are reuired for n=0
if n=1, then DFA should accept { a,b}
total 3 states are reuired for n=1
if n=2, then DFA should accept { aa,ab,ba,bb}
total 4 states are reuired for n=2
Answer: Logical
Explanation
Answer: (a) Timeout
Explanation :
DB2 allows you to put a limit on the amount of time you’ll wait at a database level using the LOCKTIMEOUT configuration parameter.
Answer: I think (B)
Progress Requirement: If no process is executing in its critical section and there exist some processes that wishes to enter their critical section, then the selection of the processes that will enter the critical section next cannot be postponed indefinitely.
Answer: (a) presentation layer
Explanation:
Layer 6:Presentation Layer
The presentation layer presents the data into a uniform format and masks the difference of data format between two dissimilar systems. It also translates the data from application to the network format. Presentation layer is also responsible for the protocol conversion, encryption, decryption and data compression. Presentation layer is a best layer for cryptography.
Network Devices: Gateway Redirector is operates on the presentation layer
(1) ∃x∀y Q(x,y)
(2) ∀x∃y Q(x,y)
Explanation:
(89) Consider unsigned integer representation. How many bits will be required to store a decimal number containing 3 digits
(8) (1) Deterministic and non-deterministic DFA's are equivalent
(2) Deterministic and non-deterministic PDA's are equivalent
which of the following are correct statements
(a) (1) only
(b) (2) only
(c) Both (1) and (2)
(d) Neither (1) nor (2)
Answer: (A)
(9)
which of the above graphs are planar.
Options
(a) G1 only
(b) G2 only
(c) Both G1 and G2
(d) Neither G1 nor G2
Answer (b)
(10) (a+b) (a+b) (a+b) ..... (a+b) n times ... minimum number of states required to implement using DFA
Options:
(a) n (b) n+1 (c) n+2 (d) None
Answer: (c)
Explanation:
if n=0, then DFA should accept only epsilon .....
if n=1, then DFA should accept { a,b}
total 3 states are reuired for n=1
if n=2, then DFA should accept { aa,ab,ba,bb}
total 4 states are reuired for n=2
(11) Length of the IPV4 header field
(12) Transaction manager functionality is
(13) Match the following
OLAP Datawarehouse
OLTP RDBMS
...............................
(14) Which of the trees needs to have all leaves in the same level
Answer: B trees
(15) which of the following tree gives sorted list during traversal
Answer: BST (Binary Search Tree )
(16) two questions from software validation and verification...
- Software verification asks the question, "Are we building the product right?"; that is, does the software conform to its specification.
- Software validation asks the question, "Are we building the right product?"; that is, is the software doing what the user really requires.
(17) CMM level 4 also included in
(a) CMM Level 2
(b) CMM level 3
(c) CMM level 5
(d) none
Answer: i think (C)
(18) A grammer has given ... four grammers given as four options . we need to find the equivalent grammer to the given grammer
(19)On a disk with 1000 cylinders, numbers 0 to 999, compute the number of tracks
(20) Question on Amdahl's law on parallel processing
It is often advised to focus system design on hardware scalability rather than on capacity. It is typically cheaper to add a new node to a system in order to achieve improved performance than to partake in performance tuning to improve the capacity that each node can handle. But this approach can have diminishing returns (as discussed in performance engineering). For example: suppose 70% of a program can be sped up if parallelized and run on multiple CPUs instead of one. If is the fraction of a calculation that is sequential, and
is the fraction of a calculation that is sequential, and  is the fraction that can be parallelized, the maximum speedup that can be achieved by using P processors is given according to Amdahl's Law:
is the fraction that can be parallelized, the maximum speedup that can be achieved by using P processors is given according to Amdahl's Law: 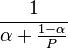 . Substituting the value for this example, using 4 processors we get
. Substituting the value for this example, using 4 processors we get 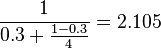 . If we double the compute power to 8 processors we get
. If we double the compute power to 8 processors we get  .
Doubling the processing power has only improved the speedup by roughly
one-fifth. If the whole problem was parallelizable, we would, of course,
expect the speed up to double also. Therefore, throwing in more
hardware is not necessarily the optimal approach.
.
Doubling the processing power has only improved the speedup by roughly
one-fifth. If the whole problem was parallelizable, we would, of course,
expect the speed up to double also. Therefore, throwing in more
hardware is not necessarily the optimal approach.
(21) java.util.*
Match the following
Calendar getTimeZone()
Random getNumber()
Timezone setId()
...................
I think...
Random getNumber()
(a) CMM Level 2
(b) CMM level 3
(c) CMM level 5
(d) none
Answer: i think (C)
(18) A grammer has given ... four grammers given as four options . we need to find the equivalent grammer to the given grammer
(19)On a disk with 1000 cylinders, numbers 0 to 999, compute the number of tracks
the disk arm must move to satisfy all the
requests in the disk queue. Assume the
last request serviced was at track 345 and
the head is moving toward track 0.The
queue in FIFO order contains requests for
the following tracks :
123,874,692,475,105,376.Perform the
computation for SCAN scheduling
algorithm :
Answer: 1219
(20) Question on Amdahl's law on parallel processing
It is often advised to focus system design on hardware scalability rather than on capacity. It is typically cheaper to add a new node to a system in order to achieve improved performance than to partake in performance tuning to improve the capacity that each node can handle. But this approach can have diminishing returns (as discussed in performance engineering). For example: suppose 70% of a program can be sped up if parallelized and run on multiple CPUs instead of one. If
 is the fraction of a calculation that is sequential, and
is the fraction of a calculation that is sequential, and  is the fraction that can be parallelized, the maximum speedup that can be achieved by using P processors is given according to Amdahl's Law:
is the fraction that can be parallelized, the maximum speedup that can be achieved by using P processors is given according to Amdahl's Law: 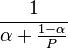 . Substituting the value for this example, using 4 processors we get
. Substituting the value for this example, using 4 processors we get 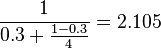 . If we double the compute power to 8 processors we get
. If we double the compute power to 8 processors we get  .
Doubling the processing power has only improved the speedup by roughly
one-fifth. If the whole problem was parallelizable, we would, of course,
expect the speed up to double also. Therefore, throwing in more
hardware is not necessarily the optimal approach.
.
Doubling the processing power has only improved the speedup by roughly
one-fifth. If the whole problem was parallelizable, we would, of course,
expect the speed up to double also. Therefore, throwing in more
hardware is not necessarily the optimal approach.
(21) java.util.*
Match the following
Calendar getTimeZone()
Random getNumber()
Timezone setId()
...................
I think...
Random getNumber()
.......................................
(22) level of abstraction, describes what data are stored in database
(a) view
(b) abstraction
(c) physical
(d) logical
Answer: Logical
Explanation
The are three levels of abstraction:
- Physical level: The lowest level of abstraction describes how data are stored.
- Logical level: The next higher level of abstraction, describes what data are stored in database and what relationship among those data.
- View level: The highest level of abstraction describes only part of entire database.
(23) hiding data and code ..........
Answer: Encapsulation
(24) Which of the following is linear data type
(a) Strings (b) lists (c) Queues (d) All the above
(25) optimal binary search tree if probability of successful and unsuccessful search are same
(26) Computational Complexity for graph coloring problem
(27) Deadlock is
(a) Timeout
(b) Timein
(c) Both a and b
(d)None
Answer: (a) Timeout
Explanation :
DB2 allows you to put a limit on the amount of time you’ll wait at a database level using the LOCKTIMEOUT configuration parameter.
(28) Software is
(a) schedule with in the budget ....
(29)A common property of logic programming languages and functional languages is:
(a) both are procedural languages
(b) both are based on λ-calculus
(c) both are declarative
(d) both use Horn-clauses
(a) both are procedural languages
(b) both are based on λ-calculus
(c) both are declarative
(d) both use Horn-clauses
Answer: I think (B)
(30) A* Algorithm ..heauristic function = g+h ......................
....................................................
(a) g=0 (b) g=1
(c)h=0 (d) h=1
(31) Question on GPS ( GLOBAL POSITIONING SYSTEM )
(32) In
unit testing of a module, it is found for a set of test data, at the
maximum 90% of the code alone were tested with the probability of
success 0.9. the reliability of the module is
a. Atleast greater than 0.9
b. Equal to 0.9
c. Atmost 0.81
d. Atleast 1/0.81
a. Atleast greater than 0.9
b. Equal to 0.9
c. Atmost 0.81
d. Atleast 1/0.81
Answer: (C)
(33) which of the following software metric does not depend on programming language
(a) LOC ( Lines of code )
(b) Function Point
(c) member of token
(d) None
(34) Reliability of a software depend on
(a) Number of errors present
(35) There is an edge between u and v.. (u,v).
shortest path from s to u is 53 and shortest path from s to v is 65
then what can you say about (u,v)
(a) (u,v) =12
(b) (u,v) >= 12
(c) (u,v) <=12
(d) (u,v) > 12
(36) which of the following is not UNIX shell
(a) Bourne Shell
(b) C Shell
(c) Net Shell
(d) Korne Shell
Answer: (c) Net Shell
(37) CTRL+C Unix .....
(a) user mode
(b) kernel mode
(c) super user mode
(38) two lines .....
(a) Histogram
(b) covariance
....................
...............
(39) Printf("%c",100)
Answer: Ascii values corresponds to 100 ( that is d )
(40) Match the following
Microcontroller 8051
..............................
..............................
(41) Match the following
Instructions addressing modes
..........................................................
...........................................................
(42) Match the following
Regular languages DFA
CSL LBA
CFL PDA
Recursive languages Turing Machine
(43) Question on Prolog ... If --else
(44) Pipeline processing .....
instruction decoding .... instruction execution ....
(45) Microcomputer consits of
(a) perpherials
(b)Micro processor
(c)
(46) Color magneta ............
Red and white
Red and black
(47) In pre-emtive scheduling algorithm if time quantum increases, effective turn around time
Answer: I think Decreases
(48) making capabilities
(a) Conditional transfer
(b) Unconditional transfer
(49) non-sharable resources
(a) Mutual exclusion
...............
.............
(50) if an integer takes 2 bytes.. what is the maximum value can be represented
(51) interrupts
(a) software
(b) Hardware
(c) internal
(d) External
(52) Relationship among claases and objects .... can be represented
(a) class diagram
(b) Object diagram
(53) Which of the following deletes the structure of the data
(a) Erase
(b) Delete
(54) when one transaction updates a database item and then
the transaction fails for some reason is called
the transaction fails for some reason is called
(a) Dirty read problem
(b) temporary update problem
(55) amplification, modulation and ....................
(56) Number of binary trees with 5 nodes
(a) 32 (b) 36 (c) 120 (d) .....
(57) Given post order traversal ... need find out the preorder traversal\
(58) Consider
the methods used by processes P1 and P2 for accessing their critical
sections whenever needed, as given below. The initial values of shared
boolean variables S1 and S2 are randomly assigned.
Method Used by P1 while (S1 == S2) ; Critica1 Section S1 = S2; Method Used by P2 while (S1 == S2) ; Critica1 Section S2 = not (S1);
Which one of the following statements describes the properties achieved? (GATE CS 2010)
(A) Mutual exclusion but not progress
(B) Progress but not mutual exclusion
(C) Neither mutual exclusion nor progress
(D) Both mutual exclusion and progress
(A) Mutual exclusion but not progress
(B) Progress but not mutual exclusion
(C) Neither mutual exclusion nor progress
(D) Both mutual exclusion and progress
Progress Requirement: If no process is executing in its critical section and there exist some processes that wishes to enter their critical section, then the selection of the processes that will enter the critical section next cannot be postponed indefinitely.
(59) if virtual address space and logical address space is same then
(60) cache memory and interleaved memory
(61) compiler generates window programming
(a) text file
(b) binary file
(c) obj file
(62) Virtual switching and packet switching
(63) base class derived class... constructor order
(64) additions done in computer
(a) CPU
(b) Memory
(c)
(65) Connect different LANS with different technologies
(a) Bridges
(b) switches
(66) Encryption and Decryption of data is done in which layer?
Answer: (a) presentation layer
Explanation:
Layer 6:Presentation Layer
The presentation layer presents the data into a uniform format and masks the difference of data format between two dissimilar systems. It also translates the data from application to the network format. Presentation layer is also responsible for the protocol conversion, encryption, decryption and data compression. Presentation layer is a best layer for cryptography.
Network Devices: Gateway Redirector is operates on the presentation layer
(67)
What is the output for above circuit
option (a) is correct
(68)
K=0;
for i=1 to n
for i1=1 to i
for i2=1 to i1
................
..........
.............
for im=1 to im-1
k=k+1
output for this program?
Answer: C(n+m-1,m)
(69) E-commerce cannot be used in
(a) House banking
(b) for evaluating employee performance
(c).......
...........
(70) if virtual address space is equal to physical address space then ...
(71) Question on COSETS
(72) How many relations are there on a set with n elements that are
symmetric and How many relations are there on a set with n elements that are reflexive and symmetric ?
Solution:
Let R be the set with n elements. Then RxR has n^2 elements in it, and the relationson R correspond exactly to the subsets of RxR, giving us 2^(n^2) relations in general.
If
the relation is symmetric, we can think of it slightly differently. Let
P2(R) be all subsets of R with 2 elements, and P1(R) be all the subsets
of R with a single element. Then all symmetric relations will
correspond exactly to the subsets of P2(R) U P1(R). Notice that P2(R) is
exactly like RxR, except the pairs aren't ordered, and it only
considers pairs with distinct x and y (the pairs where they aren't
distinct are covered by P1(R)). How many elements does P2(R) have in it?
Well, we are looking for all pairs of the form:
{x, y}
where x and y are distinct and in R. They correspond to an unordered selection of 2 objects from n objects, giving us:
n C 2 = (1/2)n(n - 1)
How
many elements of P1(R) are there? Well, clearly, there will be n
elements. So, the total number of elements in P2(R) U P1(R) will be:
(1/2)n(n - 1) + n
= (1/2)n[(n - 1) + 2]
= (1/2)n(n + 1)
And, we want the number of subsets of this, so we get:
2^[(1/2)n(n + 1)]
As
for all relations that are antisymmetric, that's a bit more tricky.
I'll have to think about that one. The relations that are neither
reflexive nor irreflexive are not too difficult to count. Assuming that n
> 0, it's impossible for a relation to be simultaneously reflexive
and irreflexive, so if we count the number of reflexive relations, and
the number of irreflexive relations, then we will not have counted the
same relation twice, and we can just subtract this number from 2^(n^2).
In
both the reflexive and irreflexive cases, essentially membership in the
relation is decided for all pairs of the form {x, x}. This leaves n^2 -
n pairs to decide, giving us, in each case:
2^(n^2 - n)
choices
of relation. That is the number of reflexive relations, and also the
number of irreflexive relations. The number of relations that are either
reflexive or irreflexive will be the sum:
2^(n^2 - n) + 2^(n^2 - n) = 2^(n^2 - n + 1)
If
we subtract this from the total number of relations, 2^(n^2), then we
get the number of relations that are neither reflexive or irreflexive:
2^(n^2) - 2^(n^2 - n + 1)
Hope that helps!
EDIT: (Fixed a small mistake previously)
OK,
I've just thought of a way to deal with the antisymmetric case. Again,
we will consider P2(R) U P1(R). We can choose freely which pairs of the
form (x, x) we want in our relation, so we can choose freely our subset
of P1(R), giving us 2^n possible contributions from P1(R). As for our
contribution from P2(R), for each {x, y} pair in P2(R), we must have
exactly one of the following three possibilities:
1) Neither (x, y) nor (y, x) is in our relation.
2) Only (x, y) is in our relation.
3) Only (y, x) is in our relation.
Each
choice for each {x, y} can be made independently of the other choices
chosen previously. Also, making two distinct choices will result in two
distinct relations, i.e. we are not counting anything twice. Therefore,
the number of contributions from P2(R) will be:
3^(n C 2) = 3^[(1/2)n(n - 1)]
The contributions of P2(R) and P1(R) are independent, so the total number of antisymmetric relations will be:
2^n * 3^[(1/2)n(n - 1)]
(73) Which data structure is used when you do the post order traversal
answer: stack
(74) what would be the top of elements in stack when u do post order traversal
23^8/23*
Answeer: 6,1
(75) which class of network provides multicasting
Answer: class D
(76) ICMP protocol presents in ------
Answer: network layer
(77) x.25 is
(a) connection oriented
(b) connection less
(c) both
(d) neither of them
Answer : (a)
Answer : (a)
(78)HTML standard
(a) ISO 8879
(79)
if an instruction takes i nano seconds ... if it takes extra j nano
seconds for every k instructions then effective access time is
Answer: i+j/k
(80) if Q(x,y) represents x+y=0 and x,y are real numbers then
(2) ∀x∃y Q(x,y)
which of the statements are true
Explanation:
Compare these two sentences: "For all x, there exists at least one y
such that Q(x,y)" and "there is at least one y such that, for all x,
Q(x,y)". Here Q(x,y) is some sentence about x and y, such as "x+y=0".
The first of these means that for all x, there is a y WHICH IS ALLOWED
TO VARY WITH EACH x which makes Q(x,y) true. So, for example, "for all
x, there exists at least one y such that x+y=0" is true because y=-x
makes it true.
that means ∀x∃y Q(x,y) is true
The sentence "there is at least one x such that, for all y, Q(x,y)"
means that there exists one x which does the job for all y of making
Q(x,y) true. This is a much tougher statement to make true! Notice that
"there is at least one x such that, for all y, x+y=0" is false for the
real numbers---there x has to be -y and must vary with y which this
sentence does not allow.
that means ∃x∀y Q(x,y) is false
(81) which of the following is preferable in software
Answer : High cohesion and low coupling
(82) link state algorithm
(83) 1000 ms then frequency
(a) 1 KHZ (b) 10 khz
(84) 10 base Tx
(85) which data structure is used for heirarchical
Answer is Tree
(86) Compare B+ tree with normal trees.. why do we use B+trees
(87) which logic family is fastest
Answer: TTL
(88) To connect diffrent technology networks
Answer: bridge
Answer: TTL
(88) To connect diffrent technology networks
Answer: bridge
(89) Consider unsigned integer representation. How many bits will be required to store a decimal number containing 3 digits
Answer: 10 bits
Explanation:
Explanation:
we have to find the lowest power of 2 that is higher than that range.
For instance, 3 decimal digits -> 10^3 = 1000 possible numbers so you
have to find the lowest power of 2 that is higher than 1000, which in
this case is 2^10 = 1024 (10 bits).







super memory yaar.........
ReplyDeletecongrats